The business models helping corporations seek a competitive edge are important in today’s business world. They help identify and leverage unique strengths, ensuring sustainable growth and differences in the market. The companies can innovate, meet customer needs more effectively, and outperform competitors. Understanding and applying these models can lead to long-term success and a stronger market position.
In this article, we'll explore one of these models, the Core Competence Model, in-depth. You'll learn what it is, how to use it, and see real-world examples of its application. We'll also discuss the model's advantages, disadvantages, and the best times to apply this strategy. You'll have a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage core competencies to drive your business forward.
First things first: What is the core competence model
The Core Competence Model of Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad focuses on identifying the unique capabilities that give companies a competitive advantage.
These core competencies should be hard for competitors to imitate and provide access to a wide range of markets. By leveraging these strengths, companies can achieve long-term success.
Core competencies are not just about what a company does well. They must also be relevant to customers and contribute significantly to the benefits of the end product. This model emphasizes the importance of integrating and leveraging these strengths across the organization. This is important to create value for customers and stakeholders.
Core Competence Model: Explained
Now, we'll explore how to identify core competencies, leverage them for market success, and sustain a competitive advantage. Understanding these aspects will help you effectively apply this model to drive your business forward.
🔍Identifying core competencies
The Core Competence Model involves pinpointing a company's unique strengths that are difficult for competitors to replicate. These competencies include specialized knowledge, proprietary technologies, and unique processes. Identifying these core competencies requires a deep understanding of the organizational capabilities and the factors that contribute to its competitive advantage.
🏁Leveraging core competencies
Once identified, core competencies should be leveraged to enter and compete in various markets. These strengths should not only be a single product or service but should have broad applications. By leveraging these competencies, companies can diversify, reduce risks, and capitalize on new growth opportunities. Thus, this will enhance their market presence.
✅Sustaining competitive advantage
Core competencies must deliver significant value to customers and be difficult for competitors to imitate. Companies should focus on continuous improvement and problem-solving mechanisms to maintain these strengths. Strategic resource allocation and regular reviews ensure that core competencies remain relevant and provide a sustainable competitive advantage in an evolving market landscape.
Core Competence model template
A Core Competence Model template helps in organizing and visualizing your company's strengths. Start by listing your identified core competencies. For each competence, note how it contributes to customer value and how difficult it is to imitate. Also, take its potential to open new markets into account.
Use the Core Competence Model template to guide strategic planning and resource allocation. By having a clear visual representation of your core competencies, you can make more informed strategic decisions. You can ensure that your business focuses on its most valuable strengths.
How to use the Core Competence Model
Let's explore how to effectively use the Core Competence Model. We'll cover identifying core competencies, evaluating their customer value, analyzing competitiveness, allocating resources, monitoring and adapting, and leveraging for growth. Understanding these steps will enable you to harness your company's unique strengths for strategic advantage.
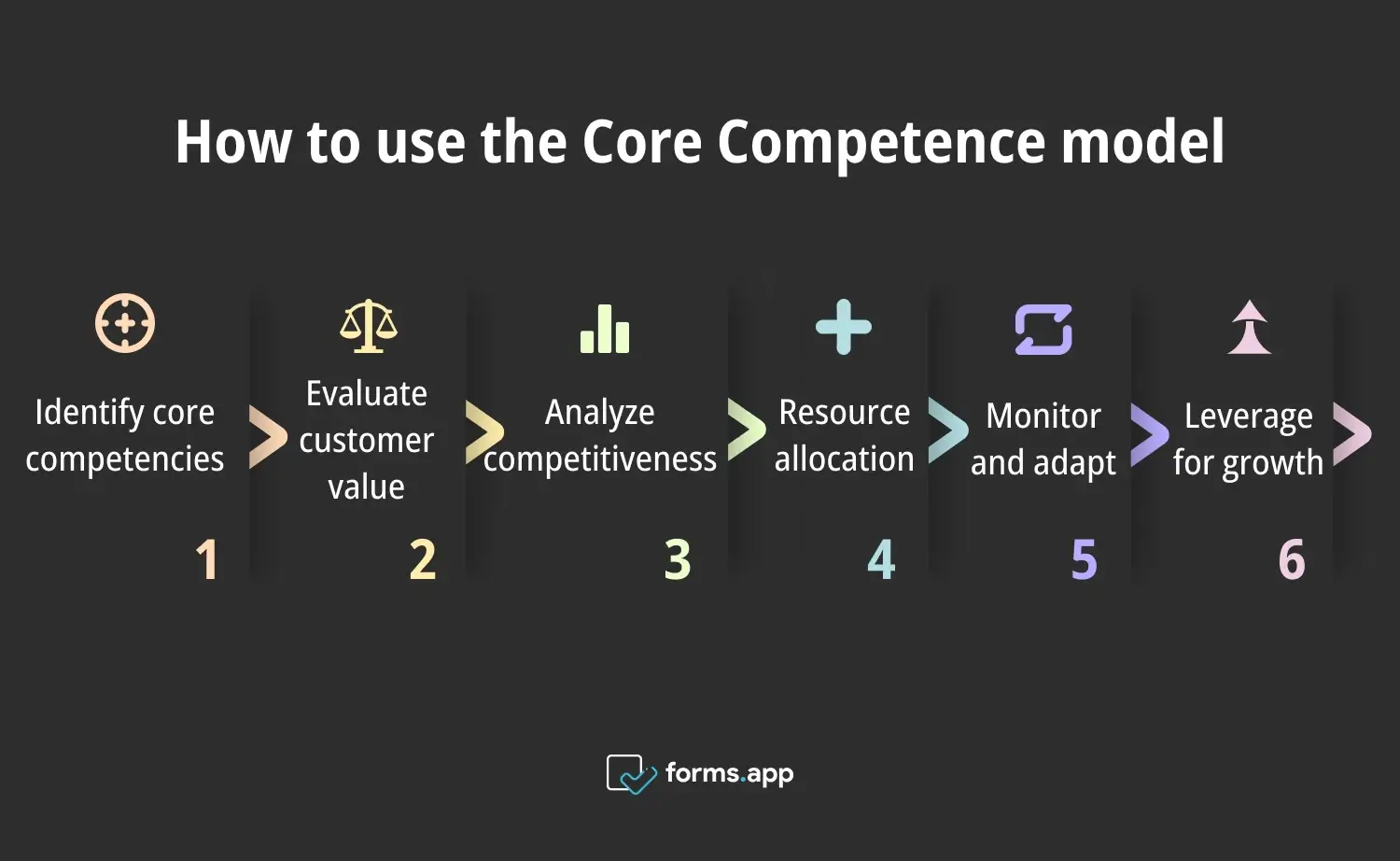
Steps to use the Core Competence model
1. Identify core competencies
Conduct an internal audit. Gather input from departments to understand your company. Look for skills, technologies, and processes that are unique/valuable. This step involves a thorough analysis of your organizational capabilities and resources.
Do not forget to keep the competitive advantage in mind.
2. Evaluate customer value
Assess how each identified competence adds value to your customers. This could be through improved product quality, better customer service, or innovative features. Ensure that these competencies align with customer needs and preferences. By understanding how your strengths benefit customers, you can enhance your value proposition and build core competencies.
3. Analyze competitiveness
Examine how difficult it is for competitors to imitate your core competencies. Consider factors such as proprietary knowledge, patents, and complex processes. The harder it is for others to replicate your strengths, the more sustainable your competitive advantage. By analyzing the competitive landscape, you can identify threats and opportunities and adjust your strategy accordingly.
4. Resource allocation
Allocate resources to enhance and maintain your core competencies. This might involve investing in new technologies, training team members, or improving processes. Ensure that resources focus on areas that will provide the most strategic benefit. By focusing on investments in core competencies, you can strengthen your competitive position and drive growth.
5. Monitor and adapt
Regularly review and update your core competencies. As markets and technologies evolve, your strengths might change. Stay agile and prepared to adapt your strategy to maintain a competitive edge. By continuously learning your core competencies, you can stay ahead of the competition and respond to market changes effectively.
6. Leverage for growth
Use your core competencies to expand into new markets. Identify opportunities where your strengths can provide a competitive advantage. This could involve developing new products, entering new geographic regions, or targeting new customer segments. You can use the core competencies in job descriptions to attract qualified job seekers.
By leveraging your core competencies, you can drive business growth and increase market share.
Advantages & Disadvantages of the Core Competence model
Let's discuss the Advantages and Disadvantages of the Core Competence Model. We'll explore how identifying and leveraging core competencies can provide a competitive edge and enhance resource efficiency. Additionally, we'll examine potential drawbacks such as over-reliance and complex implementation, ensuring a balanced understanding of this strategic framework.
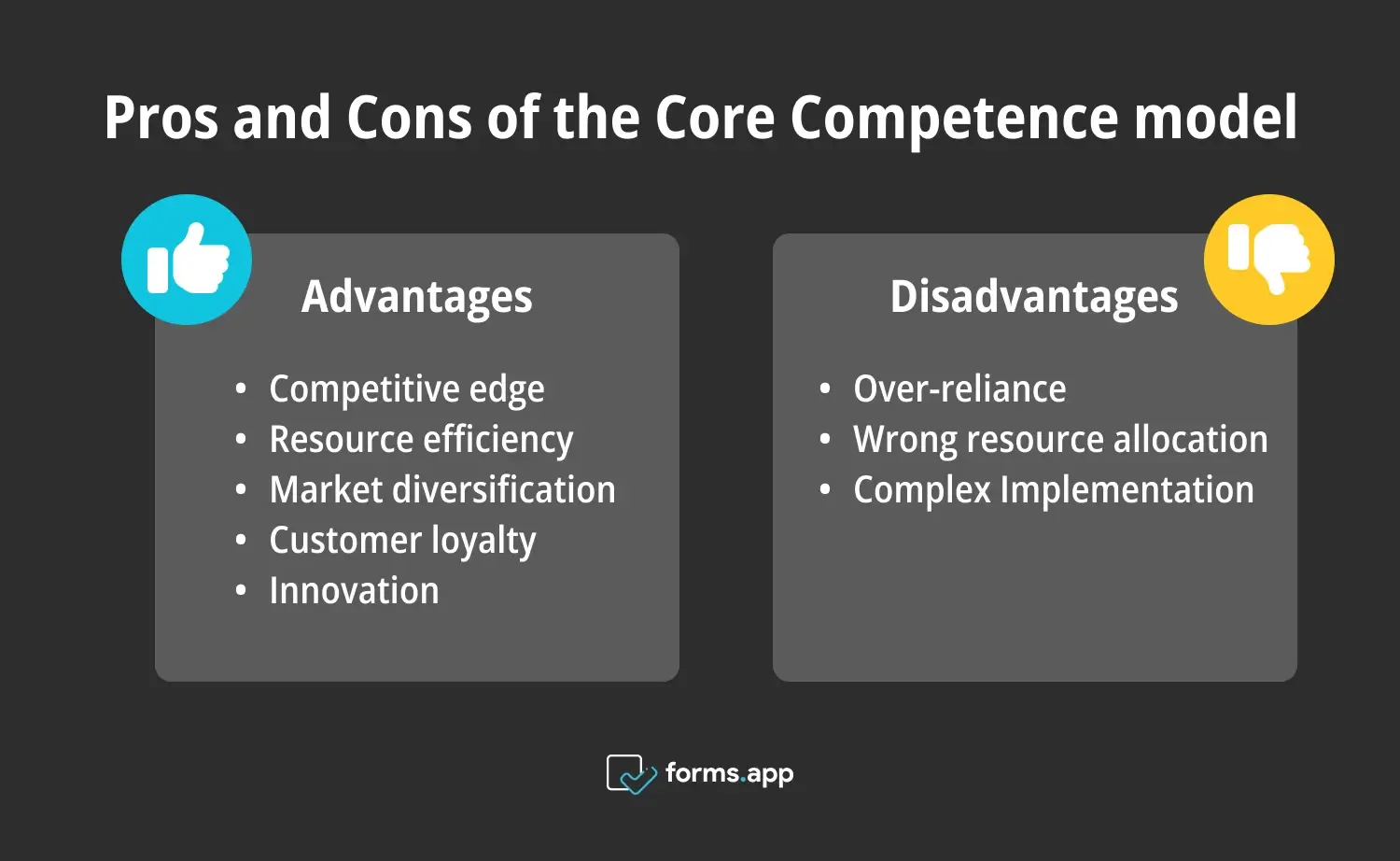
Pros and Cons of the Core Competence model
Advantages:
➕Competitive edge: Identifying and leveraging core competencies provides a significant competitive advantage. Companies can focus on their unique strengths, such as active listening and conflict resolution. This leads to increased market share and profits.
➕Resource efficiency: The model helps in efficient resource allocation. By focusing on core competencies, companies can avoid wasting resources on non-strategic areas. This ensures that investments remain in areas that provide the most benefit.
➕Market diversification: Core competencies enable companies to enter and compete in multiple markets. This diversification reduces business risk and opens up new revenue streams. By leveraging their strengths, companies can explore new opportunities and drive growth.
➕Customer loyalty: By delivering superior value, companies can build strong customer loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to return and recommend the company's products or services. This leads to increased sales and long-term business success.
➕Innovation: Focusing on core competencies encourages continuous improvement and innovation. Companies stay ahead of the competition by constantly enhancing their unique strengths. This leads to the development of new products and services that meet changing customer needs.
Disadvantages:
➖Over-reliance: Focusing too much on existing competencies can lead to complacency. Companies might miss new opportunities or fail to adapt to market changes. This can result in a loss of competitive advantage.
➖Wrong resource allocation: Wrongly identifying core competencies can lead to poor resource allocation. Investing in the wrong areas can weaken the company's competitive position. It is crucial to accurately identify and prioritize core competencies to avoid this risk.
➖Complex Implementation: Identifying and leveraging core competencies can be complex and time-consuming. It requires thorough analysis and strategic planning, which might be challenging for some companies. Effective implementation requires commitment and resources.
When to use the Core Competence Model
Let’s discover when to use the Core Competence Model. We'll discuss the specific environments for this model. Understanding these contexts will help you determine the best times to apply this model. You will be able to enhance your company's competitive position and achieve strategic objectives.
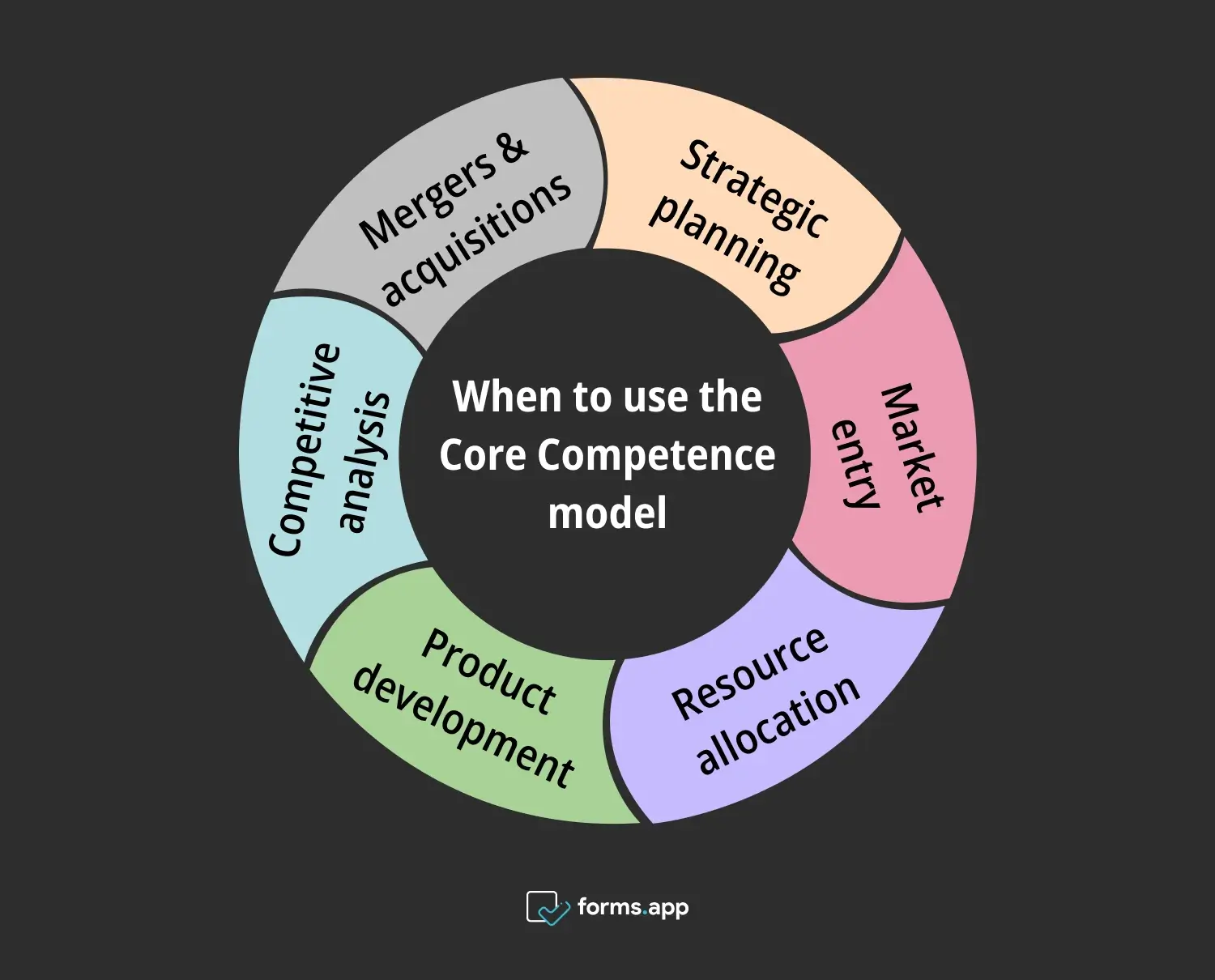
Right times to use the Core Competence model
⏰Strategic planning: Use the model during strategic planning to identify and leverage your company's strengths. This ensures that your strategy builds around unique capabilities that provide a competitive edge. By focusing on core competencies, you can develop a strategic plan that drives long-term success.
⏰Market entry: When entering new markets, use the model to assess how your core competencies can provide an advantage. This helps identify opportunities where your strengths can be most effective. You can increase your chances of success in new markets. You can also improve your performance management.
⏰Resource allocation: Apply the model when deciding where to allocate resources. Focus investments on areas that enhance your core competencies to maximize strategic benefits. Keep in mind the employee performance to maintain the core competence of the corporation.
⏰Product development: Use the model during product development to ensure new products leverage your core competencies. This increases the likelihood of success by aligning with your company's strengths. By focusing on core capabilities, you can develop innovative products that meet customer needs and drive growth.
⏰Competitive analysis: Apply the model to analyze competitors. Understanding their core competencies helps in identifying their weaknesses and finding ways to outperform them. By leveraging your own strengths, you can gain a competitive advantage and increase market share.
⏰Mergers & acquisitions: Use the model to evaluate how the new entity's core competencies will integrate with your own. This helps in making informed decisions that enhance overall competitive advantage. By focusing on core competencies, you can ensure that mergers and acquisitions strengthen your business strategy.
Examples of the Core Competence Model in Action
Let's explore how companies like Apple, Toyota, and Google leverage their core competencies, such as innovation, operational efficiency, and technological prowess. They are able to achieve market dominance and sustain competitive advantage. These Core Competency Model examples illustrate the practical application and effectiveness of the Core Competence Model.
Apple Inc.
Apple's core competencies include innovative design and a strong brand. These strengths allow Apple to dominate multiple markets, from smartphones to computers. Their design expertise and brand loyalty are hard for competitors to replicate. By focusing on these core competencies, Apple has built a loyal customer base and achieved long-term success.
Toyota
Toyota's core competencies are its efficient manufacturing processes and high-quality standards. These capabilities enable Toyota to produce reliable vehicles at competitive prices. Their focus on continuous improvement makes these competencies difficult for competitors to match. By leveraging these strengths, Toyota has become a leader in the automotive industry.
Google's core competencies are its search algorithms and data analysis capabilities. These strengths underpin their dominance in the search engine market and support their ventures into advertising and cloud services. Competitors struggle to match Google's technological prowess. By focusing on these core competencies, Google has maintained its position as a leading technology company.
Frequently asked questions about the core competence model
Now, we will address frequently asked questions about the subject. We will cover the top four competencies and the competence model theory of Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad. We will also look at the core competency framework used to identify and leverage organizational success. These answers will provide a clear understanding of this strategic concept.
The top four competencies typically include innovation, customer focus, operational efficiency, and leadership. Innovation involves developing new ideas and products. Customer focus ensures meeting and exceeding customer expectations. Operational efficiency enhances processes to reduce costs and improve quality.
Gary Hamel and C.K. Prahalad came up with this model in their article of 1990 in Harvard Business Review. It emphasizes identifying and leveraging a company's unique strengths that provide a competitive advantage. These core competencies should be valuable, rare, and hard to imitate. It enables the company to access a wide range of markets and create significant customer value.
The core competency framework is a strategic tool used to identify and organize a company's key strengths. It involves analyzing skills, technologies, and processes that are unique and valuable to the company. This framework helps in strategic planning and resource allocation. It also ensures the company's capabilities align with market opportunities and customer needs.
Final words
Understanding and leveraging the Core Competence Model is crucial for business success. By focusing on unique strengths, companies can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge. This model helps identify, enhance, and leverage core competencies to drive long-term success.
In this article, we've covered the Core Competencies’ meaning in detail. We have seen its pros and cons and suitable environments. We have also witnessed the core competencies examples of well-known companies. Apply these insights to identify and leverage your company's strengths and ensure long-term success and market leadership.
Fatih is a content writer at forms.app and a translator specializing in many text domains, including medical, legal, and technical. He loves studying foreign languages. Fatih especially likes to create content about program management, organizational models, and planning tools.
- First things first: What is the core competence model
- Core Competence Model: Explained
- Core Competence model template
- How to use the Core Competence Model
- Advantages & Disadvantages of the Core Competence model
- When to use the Core Competence Model
- Examples of the Core Competence Model in Action
- Frequently asked questions about the core competence model
- Final words